fluorescence polarimeter polarized light|polarimetry pdf : exporter In a polarimeter (figure 2), plane-polarized light is introduced to a tube (typically 10 cm in length, figure 3) containing a solution with the substance to be measured. If the substance is optical inactive, the plane of the polarized light will not change in orientation and the observer will read an angle of [α]= 0 o. If the compound in the . Desenvolvemos soluções completas para gestão pública, not.
{plog:ftitle_list}
webNo não me mate meu irmão portal Zacarias, você encontrará uma ampla gama de temas e assuntos sendo abordados. Desde notícias sobre entretenimento, como lançamentos de filmes e séries, até discussões sérias sobre política e economia, o portal Zacarias cobre todas as áreas de interesse do público.
In other areas, polarimetry can be used to characterise the vectorial information of fluorescence dyes, as the dipole orientation of the fluorophore is encoded in the polarisation state of.
Fluorescence anisotropy or fluorescence polarization is a measurement of the changing orientation of a molecule in space, with respect to the time between the absorption and emission events.
The seedlings were grown under a fluorescent lamp (TLD 32 W/865RS, Philips) where the photosynthetic photon flux density (PPFD) was 210 ± 10 μmol/m 2 s −1 and the photoperiod was 16 h light .In a polarimeter (figure 2), plane-polarized light is introduced to a tube (typically 10 cm in length, figure 3) containing a solution with the substance to be measured. If the substance is optical inactive, the plane of the polarized light will not change in orientation and the observer will read an angle of [α]= 0 o. If the compound in the . Light, as an electromagnetic wave, possesses several fundamental properties, which include intensity, wavelength, phase and polarisation 1,2 (see Fig. 1a).While the former three are scalar .
A polarimeter typically comprises of a light source, polarizer, sample cell, analyzer, and detector. The gadget works on the basis of optical rotation and utilizes polarized light law. The light emitted by the source is first filtered by a polarizer, which polarizes the light waves in a certain plane. Circularly polarized light (CPL), also known as spin light, plays an important role in various contemporary applications such as chiral molecule distinguishing 1, remote sensing 2, quantum optics . The polarized light passes through the sample tube and exhibits angular rotation to the left (-) or right (+). The amount of rotation is measured by the graduated circle or by a digital sensor. The specific rotation of a substance is a physical property that is dependent on the wavelength of light, the temperature, and the concentration of the . The inherent properties of light are a significant source of information when used to probe the properties of vegetal tissues 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17.In microscopy imaging, it is .
super resolution fluorescence polarization
Fluorescence polarization (FP) is a fluorescence-based detection method that is widely used to monitor molecular interactions in solution. Unlike fluorescence intensity which focuses on the quantification of emission intensity at a specific wavelength and neglects its polarization, fluorescence polarization specifically analyses as output the emission intensity of different . The device that selects plane-polarized light from natural or unpolarized light is called a polarizer. The Principles behind Polarized Light Microscopes. In a polarized light microscope, a polarizer intervenes between the light source and the sample. Thus, the polarized light source is converted into plane-polarized light before it hits the sample. To generate a polarized light beam, automatic polarimeters typically use a monochromatic light source, such as a sodium (Na) lamp or light-emitting diode (LED). The use of monochromatic light guarantees that measurements are consistent. Polarizer; The polarizer is a critical component that converts unpolarized light from the source into a .
polarimetry sample
Fluorescence polarization microscopy images both the intensity and orientation of fluorescent dipoles and plays a vital role in studying molecular structures and dynamics of bio-complexes. However . CPL can be best described by comparing it to CD, which involves a difference in the amount of absorption of left- and right-handed circularly polarized light by an optically active substance, as shown in Fig. 14.1a.In contrast, as shown in Fig. 14.1b, CPL spectroscopy measures the difference in the intensity of left- and right-handed circularly polarized .
Understanding the Basics of a Polarimeter. A polarimeter is a device that detects the rotation of plane-polarized light as it passes through an optically active substance. This substance could be in the form of a liquid, a solid, or a solution. The degree of rotation is proportional to the optically active compound concentration and the length of the sample tube. A linear detection response is observed by both polarimeter and fluorescence spectrometer in a wide range 0–0.28 g/ml of sugar. These results depict that PLRA polarimeter is novel, remote, precise and cost-effective for quantitative determination of optically active ingredient in the host solution. . T is the transmittance of the light beam .
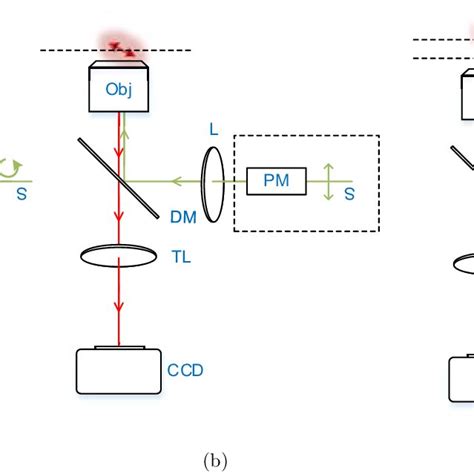
The difference between the two techniques is that linear dichroism obtains the fluorescence polarization through excitation modulation with linearly polarized excitation light, while fluorescence . Schematic experimental setup of the fast adaptive polarimeter. Light from a collimated LED source is deflected by the dichroic mirror of a CYT5 fluorescence cube. Then it is linearly polarized by a horizontal polarized (LHP) modulated by a variable Liquid Crystal Retarder whose fast axis is rotated 45 ° CCW with respect to LHP. The modulated .A polarimeter [1] is a scientific instrument used to measure optical rotation: . When plane-polarised light passes through some crystals, the velocity of left-polarized light is different from that of the right-polarized light, thus the crystals are said to have two refractive indices, i.e. double refracting. .
Polarized light microscopy (PLM) is a common but critical method for pharmaceutical crystallinity characterization, which has been widely introduced for research purposes or drug testing and is recommended by many pharmacopeias around the world. To date, crystallinity characterization of pharmaceutical solids is restricted to laboratories due to . Schematic experimental setup of the fast adaptive polarimeter. Light from a collimated LED source is deflected by the dichroic mirror of a CYT5 fluorescence cube. Then it is linearly polarized by a horizontal polarized (LHP) modulated by a variable Liquid Crystal Retarder whose fast axis is rotated 45 ° CCW with respect to LHP. The modulated . To preserve spatial resolution in polarimetry microscope, numerical aperture of polarized light objectives is usually 10–25% higher than those for ordinary microscopes. Furthermore, objectives designed for polarized light microscopy must be stress- and strain-free to prevent image quality loss . In general, there are two sources of .
Circularly polarized light (CPL) carrying photons with spin angular momentum has attracted a wide range of interests for its practical applications in circularly polarized ellipsometric tomography .Fluorescence polarization measurements provide information on molecular orientation and mobility and processes that modulate them, including receptor–ligand interactions, protein–DNA interactions, proteolysis, membrane fluidity and muscle contraction (Figure 1).Because polarization is a general property of fluorescent molecules (with certain exceptions such as .Polarized light with its electric field along the plane of incidence is thus denoted p-polarized, while light whose electric field is normal to the plane of incidence is called s-polarized. P -polarization is commonly referred to as transverse-magnetic (TM), and has also been termed pi-polarized or π -polarized , or tangential plane polarized .
paint test equipment congleton indeed
Interactions between lone pairs and aromatic π systems are significant across biology and self-assembled materials. Herein, employing an achiral confinement metal–organic framework (MOF) encapsulates guest molecules, it is successfully realized that lone pair (lp)-π interaction induces fluorescence “turn-on” and circularly polarized luminescence for the first time.
Polarizing microscope operating principle Depiction of internal organs of a midge larva via birefringence and polarized light microscopy. Polarized light microscopy can mean any of a number of optical microscopy techniques involving polarized light.Simple techniques include illumination of the sample with polarized light. Directly transmitted light can, optionally, be .Fluorescence polarization microscopy images both the intensity and orientation of fluor- escent dipoles and plays a vital role in studying molecular structures and dynamics of bio- complexes. Polarimetry is a technique used to measure the rotation of polarized light as it passes through a sample.It is based on the principle that certain substances, such as chiral molecules, rotate the plane of polarization of light. In this article, we will explore the principles of polarimetry, its applications, and the trends shaping the industry.
polarimetry pdf
Rocket League® . /en
fluorescence polarimeter polarized light|polarimetry pdf